Which VPN or purpose-built software did you use to visit websites on the deep or the dark web? For other guides related on enhancing your privacy when accessing the hidden web, check out our article on I2P vs Tor. By now, you know what the deep and the dark web have in common and what sets them apart. Understanding how these parts of the internet work helps you protect your security and privacy as you navigate them. Payment for these services is generally made using difficult-to-trace digital currency, such as Bitcoin.
Dark web monitoring is when a tool is used to scan the dark web for your personal information such as your email address or credentials. This can be done manually with a free service that doesn’t notify you, or it can be done automatically with a tool that detects and notifies you when your credentials are being sold on the dark web. Right at the top of the internet is the surface web, which is made up of everything you can access with everyday browsers and search engines. But below the surface lies the deep web — the parts of the internet that aren’t indexed. So they’re right there on the internet, but you can’t find them by doing a quick search. While it may come as a surprise to some, about 7,500 terabytes of all the information on the internet is on the deep web, compared to only 19 terabytes on the surface web.
- The deep web is generally safe and secure to use; owners of private websites or services are responsible for maintaining their security.
- Technically speaking, the dark web is the content existing on darknets, closed-off networks that exist on top of the regular internet and use its infrastructure.
- Deep and Dark Web are two different concepts, but easy to understand.
- Now, let’s explore their differences in more detail, how to access them, and dispel some misconceptions along the way.
- Depending on your needs, you may want to use your VPN to download the secure browser of your choice.
One-stop Solution To All Log Management And Active Directory Auditing
In addition, there is always a malware risk in that uncharted territory. The dark web is home to stolen identities, credit cards, national IDs, passports, etc. And since we can’t access every dark web onion site to see if our own credentials are up for sale, we have some monitoring tools embedded within NordVPN and 1Password.
Typical Deep Web Content:
Instead, it passes user data through a randomized link of encrypted servers called nodes. ‘The Onion Routing’ (Tor) is a project that has led to the creation of the Tor browser, making it easy for even regular web users to visit the dark web. The terms dark web and deep web are perceived to be linked with illegal and otherwise suspicious activity; however, a vast difference exists between the two. All web pages not indexed by web crawlers are considered to be a part of the deep web. The content is generally more secure and clean than that of the surface web. If the surface web is the visible part of an iceberg above water, the deep web is the part submerged beneath – much larger but hidden from plain view.
What Are The Differences Between The Deep And Dark Web?
They offer a place for threat actors to connect and discuss tactics, sell stealer logs, and more. Indexing is how search engines such as Google analyze and store data on websites, allowing them to appear when you search for them. While the deep web is definitely safer than the dark web and its criminal activities, some unindexed sites may contain the same threats. In fact, since the deep web can be accessed from a regular browser, you actually have to be more careful. When most people talk about the deep web, the conversation often turns to nefarious or malicious uses.
Below the surface of the internet — whose web pages are indexed by popular search engines — exists something called the deep web, and further below that, the dark web. We can’t discuss the history of the dark web without understanding the history of TOR, the most popular dark web network. The principle of ‘onion routing’, which underpins TOR, was developed by the researchers Paul Syverson, Michael G. Reed and David Goldschlag at the United States Naval Research Laboratory in the 1990’s.
Web Hosting Company Increases Security Team Bandwidth With Up To 80% Decrease In Threat Research Times
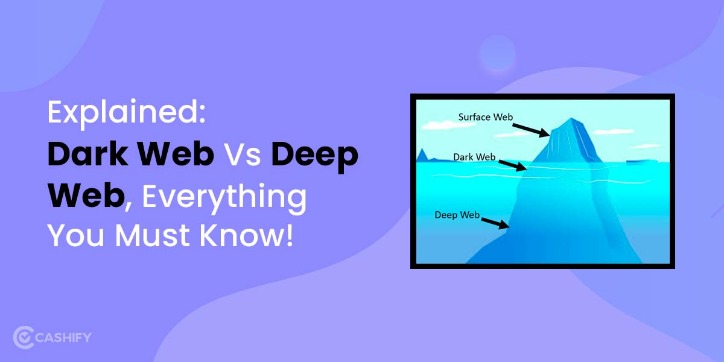
That hidden portion lives across the Deep Web, Dark Web, and Darknet. These terms are often confused or misused, but they describe very different layers of the Internet. You’re only scratching the surface when you use the Internet for daily activities—reading news, managing finances, running businesses. Search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo can access just about 4% of the web.
Get The Latest Insights, Trends And Security News Subscribe To CyberheistNews
Do you want to know the difference between the deep web and the dark web? While these two terms are often used interchangeably, the deep web and dark web are not the same. The dark web is a part of the deep web, but not everything on the deep web is part of the dark web.
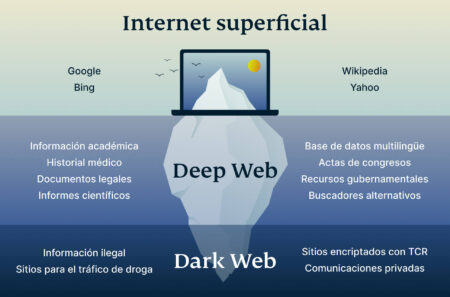
- It comprises many legitimate resources including academic databases, medical records, and private corporate networks.
- As a rule, this side of the internet hides content, identities, and locations from third parties that are common throughout the ‘surface web’ (mainstream, public websites).
- Organizations should establish clear policies governing the acceptable use of anonymizing technologies by employees.
- Before diving deeper into the differences between the Deep Web and Dark Web, it is essential to understand the general structure of the internet.
- Start a free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager today to begin securing your accounts from common cyber threats on all parts of the internet.
How To Safely Access The Dark Web?
On the dark web, neither users nor web administrators reveal themselves to each other, including their identity or their location. Hence, it’s very hard to shut down dark web servers or place geo-restrictions on users. The deep web is largely used to protect personal information, safeguard databases and access certain services, whereas the dark web is often used to engage in illegal activities. It is also used for military/police investigations, political protests and anonymous internet browsing. The deep web resides just beneath the surface web, and it comprises content and services largely inaccessible to regular internet users. Though some content and services on the deep web are obscured through non-indexing, the majority are hidden through paywalling and password protection.
The next layer is the “deep web,” a large invisible portion of the Internet. We call these websites “deep,” as the content is hidden, and search engines don’t index them. For example, your Web-based email inbox, online banking, checkout and payment pages, and restricted pages, such as website post drafts, company intranets, and government and military databases. Accessing Deep Web content typically involves straightforward login procedures rather than specialized software. Search engines use automated programs known as “web crawlers” or “spiders” that systematically scan webpages, indexing their content. Any website or page that’s not behind a paywall, login, or specialized network protocol can be included in these indexes.
What Is Threat Hunting?
That’s a deliberate ploy so that only browsers with specific proxies are allowed to access those sites. It’s also very difficult to remember the URLs of sites on the dark web, which is another way to maintain their anonymity. Bitsight’s 2025 deep web intelligence shows how cybercriminals are multiplying, diversifying—and getting smarter. Fraudsters who have hacked into systems and stolen data oftentimes turn to the Dark Web to sell what they’ve gathered. Common items for sale include credit card data, credentials, and even fingerprints. The price tag for these items may be surprising, with usernames and passwords selling anywhere from $.10 to $1 and fingerprints selling for about $2 each.
This dichotomy reminds us of the necessity for awareness, the potential for misuse, and the vital importance of data security, ethics, and legal frameworks in our increasingly digital lives. As technology continues to evolve, so will the landscape of both the Deep Web and Dark Web, demanding ongoing scrutiny and understanding from all internet users. The “onion routing” technology underpinning the dark web was developed by researchers at the U.S.
The Internet Is Not The Web
However, while the internet includes a lot of data we don’t usually see (deep web), the dark web has a reputation for concealing and facilitating criminal activities. While both the dark and deep web represent parts of the internet that fall outside the scope of traditional search engines, they differ in accessibility, use cases, and the types of threats they expose. Unlike the dark web, you don’t need any special software to access the deep web and can use your usual browser.